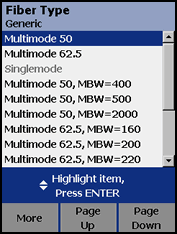
MBW is an abbreviation for Modal Bandwidth. You will see this when selecting Fiber Type in the SETUP menu.
The modal bandwidth of the fiber cable will determine the length you can run an application. This is particularly important when implementing Gigabit Ethernet over 62.5/125 m multimode fiber.
-
62.5/125 µm multimode fiber
Modal Bandwidth = 160MHz.km @ 850 nm
Max. distance for Gigabit Ethernet = 220 meters
-
62.5/125 µm multimode fiber
Modal Bandwidth = 200MHz.km @ 850 nm
Max. distance for Gigabit Ethernet = 275 meters
If you are not sure what the MBW is for the cable installed, then you must be conservative and assume the worst. Therefore, select MBW = 160.
Modal Bandwidth a brief explanation
As the individual pulses of light which make up a digital signal travel along the fiber, they will suffer some distortion. In multimode (larger core) fibers, this is due to the energy traveling in different modes, so some of the light energy in a pulse travels along a longer path than other parts of the pulse. This is called modal dispersion and is the limiting factor of the bandwidth of a multimode fiber.
The bandwidth of a multimode fiber is expressed in units of MHz.km. Note that this is a frequency multiplied by a distance. This means that either a low bandwidth signal may be transmitted over a long distance or a high bandwidth signal may be transmitted over a short distance.
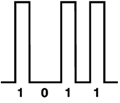
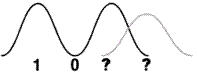
If the pulse spreads too much, the receiver will become confused as shown below.
Caution
You may well be able to install a link that is 350 meters with 62.5/125 m multimode fiber and meet the loss budget dictated by IEEE 802.3z of 2.38 dB. However, it may not support Gigabit because the modal bandwidth of the fiber is not high enough.
|








